What’s new in SQL Server 2014
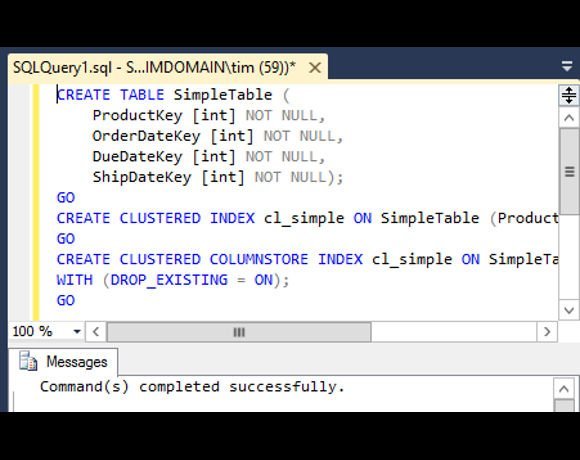
SQL Server in-memory columnstore indexes, introduced in SQL Server 2012, store data in a column-wise format. This is ideal for scanning large data sets, such as data warehouse queries, especially when only a few columns are required. It also enables excellent data compression since columns often contain similar data.
Microsoft claims up to 10 times query performance gain, and up to seven times data compression. There are some limitations on the type of data that can be indexed, with text, image, varchar and some others disallowed.
In SQL Server 2012, the columnstore indexes are non-clustered and cannot be updated other than by rebuilding the entire index. SQL Server 2014 introduces clustered columnstore indexes, which become the primary storage method for the table. These can be updated, but cannot be combined with any other indexes. There is also a new batch-mode query execution feature which greatly reduces CPU use. This translates to faster and more efficient use of SQL Server in data warehouse applications.