Getty Images/iStockphoto
2022 becomes ‘graduation year’ as 5G reaches global tipping point
Seventh annual 5G progress report from provider of network test, monitoring and assurance solutions finds 47 of world’s 70 largest economies now have active 5G networks, with diverse and widespread interest in mmWave across the globe
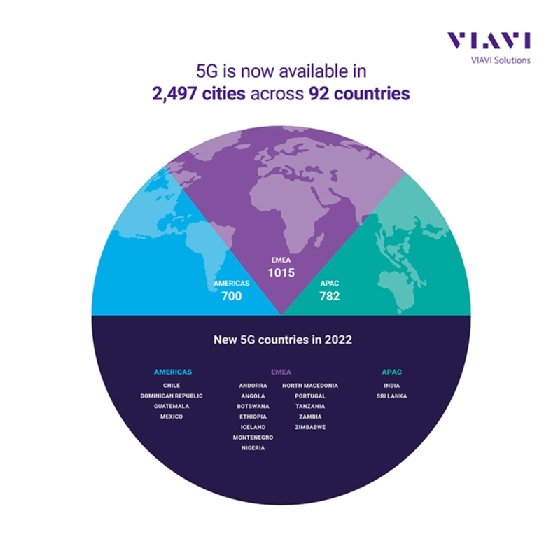
Industry data from Viavi Solutions has revealed just how hot 5G was in 2022, evolving from being a developed markets offer into a global phenomenon, with 5G networks now active in 47 of the world’s 70 largest economies by GDP and 2,497 cities across 92 countries globally having commercial 5G networks.
The seventh annual The state of 5G report also showed a further 23 countries have pre-commercial 5G trials underway and 32 countries have announced their 5G intentions. This leaves just 48 countries, many of which are smaller island nations, that have not publicly announced plans for 5G, said Viavi.
A total of 18 countries announced their first 5G deployments in 2022. These include two of the largest developing economies, India and Mexico, as well as other emerging economies such as Angola, Ethiopia and Guatemala.
Yet perhaps of most interest is the fact that the superpower clash between the US and China is extending to 5G, with the former displacing the latter in the 5G cities leaderboard for the first time.
The number of US cities with 5G networks has grown significantly to 503, compared with just 297 in May 2022 – a 69% increase. In contrast, the number of 5G cities in China has remained static at 356 since Viavi’s June 2021 update. Yet China was ahead in other key metrics.
The breadth of 5G coverage in the US contrasts with China’s depth of 5G coverage, with China remaining ahead in data speeds, 5G subscribers and base stations deployed.
Confirming a trend that has only become more pronounced since the turn of the year, the study found that the manufacturing sector has emerged as a clear leader in private 5G, with 44% of the publicly announced deployments, followed by logistics, education, transport, sports, utilities and mining.
This trend appears to suggest a clear pragmatism about how the business world is tackling private 5G, where organisations with the biggest connectivity pain points and greatest opportunities for smart applications are naturally emerging as the private 5G front-runners.
Viavi noted that businesses within these sectors often operate in challenging environments where high-speed connectivity may not be a given. These verticals also cross over with the sectors where internet of things (IoT) applications have evolved most strongly, leading to discussions of smart factories, smart cities and so on. It added that the close relationship between private 5G and IoT opportunities also coincided with a new realism among telecoms operators about IoT being an almost entirely vertically focused revenue opportunity.
The report also showed that standalone (SA) 5G was gaining momentum, with 45 SA 5G networks in place across 23 countries by January 2023. This contrasted with January 2022, when there were just 24 NSA networks globally. In addition, the study highlighted the diverse and widespread interest in mmWave across the globe.
Spectrum for 5G in the mmWave band, generally considered to be 24GHz and above, has garnered a lot of interest from diverse countries. Those that have made mmWave spectrum available span every continent and represent a mix of population sizes, economies and levels of technological advancement. Several of the largest mobile markets in the world, including China, India and the US, have made mmWave available, as well as those with tiny populations such as Seychelles and Guam.
Viavi observed that the diversity of countries licensing mmWave shows there is a clear appeal from regulators combined with a natural interest from spectrum-hungry operators. Nonetheless, with clear benefits and drawbacks, the mmWave story is likely to have many twists and turns over the coming years.
“2022 was 5G’s graduation year,” commented Sameh Yamany, CTO at Viavi Solutions. “On a technical level…with a near doubling of standalone 5G networks, the capabilities of 5G have expanded significantly and we can look forward to more sophisticated network and business capabilities from operators. In the coming year, a major focus will be network quality and the further development of Open RAN technologies – and we’ll be playing our part in ensuring those are as successful as possible.”
Read more about 5G
- AMRC demos UK’s first, fully operational standalone 5G factory of the future: Centre for research into advanced manufacturing technologies used in the aerospace, automotive, medical and other high-value manufacturing sectors shows transformative effect of standalone 5G in £10m+ UK government-backed project.
- Study reveals major application areas driving the growth of low-loss materials market for 5G and 6G in CPEs, forecasting future revenue and area demand for low-loss materials for 5G.
- Study shows mobile users in London see the smallest uplift from 5G in terms of download speeds compared with more rural regions, but also that there is little difference in the uplift in average download speeds seen by users in rural and urban areas with 5G compared with 4G.